Technology plays a vital role in conservation efforts to protect the planet. Advanced tools and innovations allow scientists and activists to better understand environmental threats, reduce further damage, and come up with long-lasting solutions.
The health of our planet is in a precarious state because of years of human-caused environmental harm like climate change, pollution, deforestation, species extinction and more.
Many of these issues escalate exponentially every year as overpopulation and unchecked industrialization persist, which will eventually cause irreversible damage to Earth’s habitable ecosystems.
Time is running out to enact meaningful countermeasures before reaching alarming tipping points forecasted by researchers.
Nonetheless, emerging technologies provide our best possibility to still correct humanity’s unsustainable relationship with nature if we act rapidly.
Advanced innovation presents tangible solutions to monitor, protect against and ultimately reduce mankind’s destructive ecological footprint.
Monitoring the Environment

Innovative devices now provide accurate, real-time tracking of land, air, and water health. Special sensors can be placed in forests, deserts, oceans, and other remote areas to collect large, helpful datasets.
For example, scientists have positioned high-tech buoys and underwater drones throughout the seas worldwide to measure water temperature, salinity, oxygen, pH, and turbidity.
The ocean findings give insight into the widespread consequences of climate change effects like coral bleaching.
Other gadgets like air quality monitors, flood detection systems and satellite imaging track pollution levels, deforestation rates, weather pattern changes, and general habitat destruction over time across biomes.
Quantitative information feeds into both policy changes and activist campaigns aimed at tangibly improving various ecological conditions.
Furthermore, emerging technology in the form of LoRa IoT devices from companies such as Blues, allows low-powered Wide Area Network (LPWAN) sensors to efficiently transmit data from almost anywhere through long-range networks up to 50km while maintaining years-long battery life.
Protecting Endangered Species
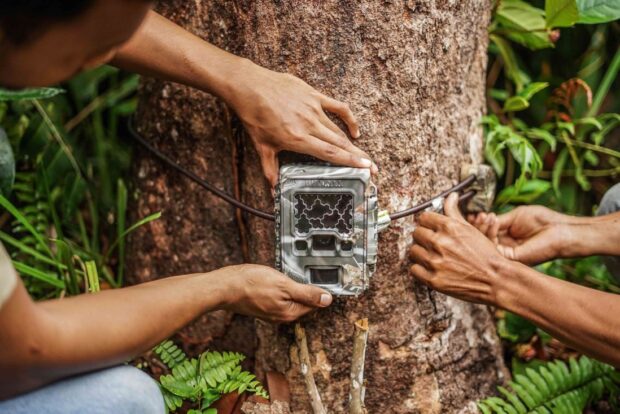

Many critical animal species face population collapse from issues like poaching, loss of natural habitats because of human activity, lack of food/prey from disappearing fellow species, and spread of diseases.
Modern technology presents several solutions that directly defend vulnerable species. Camera traps with automatic sensors can capture rare footage of elusive animals that inform protection tactics in the wild.
GPS tracking tags of migrations uncover patterns and needs for conservation planning when building green infrastructure in developing regions.
Managing Natural Resources
Beyond monitoring environments and guarding wildlife, innovations in natural resource management also promote sustainability on a global scale. Satellite imaging enables precise tracking of available freshwater stores, alerting regions at risk of a shortage.
New desalination methods deliver clean drinking water affordably using solar farms in arid places.
Automated permaculture greenhouses reuse irrigation water and redirect natural sunlight to grow robust crops year-round, even in extreme temperatures.
Such technology allows communities to prosper reliably despite common heat, drought, and shortened seasons caused by climate change effects.
Responsible resource design is paramount for civilizations to endure environmental pressures.
Promoting Sustainability

Beyond gathering intelligence, technology actively minimizes mankind’s environmental footprint across industries when adopted properly.
Smart power grids leverage real-time analytics to predict, balance, and streamline electricity use to match demand, thus lowering energy waste.
Sustainable architecture projects increasingly harness solar, wind, geothermal, and other natural sources to cleanly power, heat, and cool buildings of all sizes.
Agricultural tech manages irrigation, fertilizers, pesticides, and machinery more precisely to prevent runoff and overuse while maintaining high crop yields.
Products made from recycled ocean plastics help cut back on single-use waste ending up in landfills and waterways.
Even ordinary citizens can calculate their personal daily household impacts with online carbon footprint tools, which then provide actionable recommendations to reduce environmental harm related to their lifestyle’s energy, food, travel, shopping, waste, etc.
The public access and adoption of such sustainable best practices grows continually thanks to digital connectivity.
Encouraging Responsible Choices
Increasing public awareness around urgent threats fuels wider personal accountability and activism regarding environmental health around the globe.
Digital media allows environmental organizations and activists to spread consciousness rapidly through mobile and web networks.
Meanwhile, creative social media campaigns centered on specific eco-friendly causes inspire mass audiences into signature petitions, policy complaints, boycotting irresponsible brands, and adopting greener habits.
Viral videos that help to highlight shrinking polar caps, deforested rainforests, filled landfills and other shocking images successfully provoke intense reactions.
Mobile apps from green non-profits provide daily lifestyle tips, volunteering opportunities, and facilitate local community organizing around sustainability issues.
Furthermore, interactive website content uses infographics, videos, and quizzes to simplify the science behind complex climate topics for the average reader.
Powerful documentary programming on streaming sites also urges viewers to rethink personal habits that harm endangered habitats and species. Technology expands these educational mediums exponentially each and every year.
The Future with Tech

Modern technology’s current capabilities already equip society with better solutions to understand and combat the climate emergency. The innovations outlined above still merely brush the surface of high-tech sustainability potential.
Emerging areas like large-scale renewable energy storage, cleaner mass transit networks, regional weather control methods, lab-grown meats, and so much more seem firmly within science fiction still but become attainable with enough targeted time, funding, and human ingenuity applied properly.
If harnessed responsibly going forward, the almost unimaginable progress on the horizon can transform civilization into a vastly more sustainable model; one that generates abundant renewable power, feeds more people using fewer resources, restores degraded environments, protects powerless species, and overall learns to thrive in balance with nature rather than at its expense.
Conclusion
Advanced tech devices and applications already supply tangible solutions to ecological threats plaguing the planet currently.
Monitoring tools gather actionable statistics for activism and legislation. Conservation tech protects vulnerable species directly.
Sustainable developments minimize environmental harm related to energy, construction, agriculture, transportation, and everyday lifestyles. Digital media rapidly spreads awareness and activates wider communities.
However, the most exciting sustainable solutions still lie ahead in future innovations if funded appropriately.
Therefore, the continuing acceleration of such technologies provides hope that humanity may still restore enough balance to its ailing home in time.